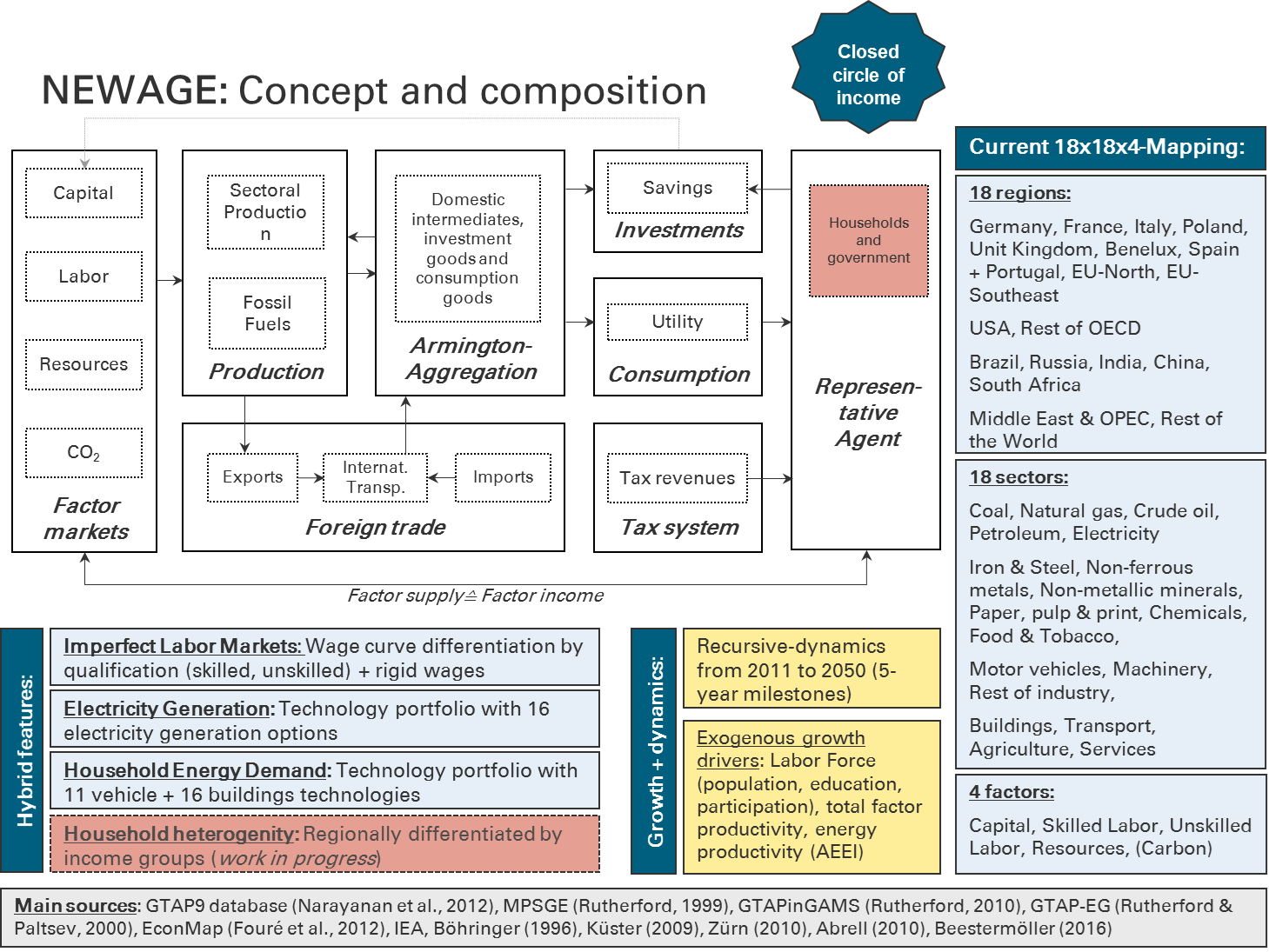
The NEWAGE (National European Worldwide Applied General Equilibrium) model is a global, recursive-dynamic Computable General Equilibrium (CGE) model with a detailed specification of the energy sector. Its main objective is to simulate and quantify macroeconomic effects of energy and environmental policy intervention in terms of its economic costs. Due to the total analytical framework of the general equilibrium approach, the interaction of actors on markets of the economy is described in a closed circular flow of income (Figure 1). This allows capturing both direct effects in individual sectors (e.g. energy) as well as indirect effects (feedback effects) across the economy that are caused by price-induced supply and demand shifts in response to the political intervention. Figure 1 illustrates the concept and structure of the NEWAGE model. Several applications were illustrated in Beestermöller 2016, Geres et al. 2016, Beestermöller et al. 2013, Beestermüller & Fahl 2013, Zürn 2010, Küster et al. 2009, Küster 2009 and Küster et al. 2007. Underlying modeling strategies are described in Böhringer 1996, Rutherford 1999, Rutherford & Paltsev 2000, Abrell 2009 and Rutherford 2010. The central external data sources are IEA 2009 and Fouré et al. 2012.